The Ultimate Organ Meat Guide
Posted by FAISAL TOOR
If you're not eating organ meats, you're missing out on nature's nutrient-dense superfoods. Beef organs are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and compounds.

Article jumplinks:
What organ meat do people eat?
Common misconceptions about organ meats
Why are grass-fed organ meats more nutritious?
What is the healthiest organ meat?
How much organ meat should I eat?
What if I don’t like eating organ meat?
Buy the best beef organ supplements
Have you heard about our grass-fed beef organ supplement? It’s an easy way to get all the nutritional benefits of organs without having to cook them yourself.
What Is Organ Meat?
Organ meats, also known as offal, are the internal organs of animals. Some people may be hesitant to try it, but offal is a nutritious and vital part of a balanced diet. These nutritional powerhouses are packed with essential amino acids, fat-soluble vitamins, and minerals that support your physical and mental health.
Organ meats also promote sustainability and respect for the entire animal. When you use the whole animal, you reduce food waste and make the most of the resources required to raise and process livestock. This approach aligns with the principles of regenerative agriculture and homesteading. Regenerative farming emphasizes sustainable and holistic practices that minimize environmental impact and promote soil health and biodiversity.
This also aligns with One Earth Health's commitment to supporting the long-term well-being of both the land and the animals raised on it. We offer high-quality beef organ supplements, ethically sourced from regenerative farms, to give you organ meats superior in their nutritional value and taste.
One of our top products is our grass-fed beef collagen supplement, crafted to support your skin, joints, and overall health. While not technically an organ, collagen provides essential support, promoting skin elasticity, joint flexibility, and overall vitality. Say hello to radiant skin, stronger joints, and improved health.
What Are the Types of Organ Meat?
You can consume pretty much the whole animal from nose to tail. Cow muscle meat such as steak and ground beef might be the most popular, but bovine organs are richer in all the nutritional goodies your body needs.
Here is a list of bovine organ meats that you can consume:
- Liver
- Heart
- Kidney
- Tongue
- Thymus gland
- Pancreas
- Brain
- Tripe (stomach)
- Oxtail
- Bone marrow
- Cheek meat
- Testicles
- Spleen
- Lungs
- Intestines
There are a some parts of the animal that people typically avoid due to potential health risks or cultural preferences. These include:
- Brain and spinal cord (may increase the risk of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), also known as "mad cow disease")
- Eyes
- Uterus and ovaries
- Adrenal glands
- Hooves and horns
Are Beef Organs Healthy?
Beef organs offer many health benefits. Here's a quick rundown of the incredible benefits of organ meats:
- Beef organs support muscle growth, repair, and maintenance, helping you build and preserve lean muscle mass.
- They help reduce inflammation, lubricate joints, and ease stiffness and discomfort.
- Bovine organs support brain health, memory, focus, and cognitive function.
- They play a crucial role in red blood cell production. Beef organs ensure adequate oxygen transport throughout the body and prevent anemia.
- Organ meats fuel energy production, reduce fatigue, and boost vitality.
- They act as immune boosters: offal fortifies the body's defenses against infections and diseases.
- Beef organs promote cell growth, collagen formation, and immune function. This aids your body in bouncing back stronger and faster from injuries.
- Beef organs support insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
- Packed with antioxidants, beef organs protect your cells from oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals.
- Organ meats are dense in nutrients that support thyroid function and regulate metabolism.
In short, beef organs are incredibly good for you. Let’s look at some of the nutrients they contain.
Nutritional Profile of Organ Meats
Beef organs contain a wealth of macronutrients, micronutrients, and other beneficial compounds.
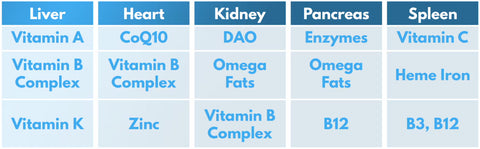
Macronutrients In Beef Organs
Beef organs are an excellent source of essential macronutrients such as protein and fat. As they are naturally low in carbohydrates, organ meats are the perfect choice for those following the keto diet. They promote and maintain a state of ketosis, which can lead to improved weight loss, increased energy levels, and better metabolic health.
Protein
Beef organs are incredibly rich in high-quality, complete protein, containing all the essential amino acids your body needs for optimal health and function. The protein content varies slightly among different organs, but on average, a single serving of beef liver contains around 20–22 grams of protein, while the same amount of beef heart tender provides about 17-18 grams.
The protein in bovine organs is highly digestible and bioavailable, so your body can easily absorb and use it for important functions, such as building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting immune health.
Lipids (Fat)
Beef organs are an excellent source of healthy fats. The liver is relatively low in fat (around 5 grams per single serving), while beef heart and kidneys contain around 10–12 grams per 100-gram serving.
The fat content of organ meats is primarily composed of:
- Monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs): known for their heart-protective and anti-inflammatory properties
- Oleic acid
- Palmitoleic acid
- Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs): essential for brain development, heart health, and reducing inflammation
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
- Omega-6 fatty acids
- Linoleic acid (LA)
- Arachidonic acid (AA)
- Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA): found in higher amounts in grass-fed beef organs; linked to improved body composition and reduced inflammation
- Phospholipids: support brain health, cell membrane function, and energy production
- Phosphatidylcholine
- Phosphatidylserine
- Saturated fatty acids
- Palmitic acid
- Stearic acid
- Myristic acid
Carbohydrates
Beef organs are naturally low in carbohydrates. Most organ meats contain only trace amounts—the liver contains only 1.1g of total carbs per 1 oz (21g) serving. Other organ meats such as the heart, kidney, and tongue have negligible amounts of carbs, typically less than 1g per single serving.
If you’re on a low-carb or keto diet, beef organs are perfect for you.
Vitamins In Beef Organs
Beef organs contain tons of essential vitamins. They provide an abundance of fat-soluble and water-soluble vitamins in highly bioavailable forms. These vitamins play crucial roles in many important bodily functions, from supporting eye health and immune function to promoting healthy skin and hair.
Offal is rich in fat-soluble and water-soluble vitamins.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins In Beef Organs
Fat-soluble vitamins are stored in the body's fatty tissues. They can accumulate in the body over time, so when you consume them in excessive amounts, you may experience an imbalance.
Here’s what you need to know about the vitamin content in beef organs.
- Vitamin A (retinol)
- Vitamin A is crucial for maintaining healthy vision, supporting immune function, and promoting skin health.
- The liver is a true vitamin A powerhouse, with just a 3.5-ounce serving providing over 300% of the daily value (DV).
- A 100-gram serving of beef kidney provides approximately 137% of the daily value (647 µg) for vitamin A. The same amount of beef heart has about 15 µg of vitamin A.

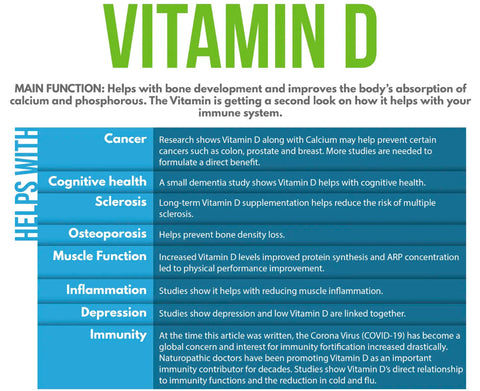
- Vitamin D (cholecalciferol)
- Referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” vitamin D is essential for strong bones, teeth, and a robust immune system.
- Beef liver contains the most vitamin D: it contains approximately 1.2 μg per 100g of raw liver (according to research).
- Kidneys offer decent amounts of vitamin D.
- Vitamin E (tocopherol)
- Vitamin E acts as a powerful antioxidant. It protects your cells from oxidative stress and supports skin health.
- It also strengthens your bones and aids muscle function, mainly by reducing inflammation in the body.
- You'll find a decent dose of this fat-soluble vitamin in beef liver, heart, and kidney, with smaller amounts in the pancreas and spleen.
- Vitamin K (phylloquinone and menaquinone)
- Vitamin K plays a vital role in blood clotting, bone health, and proper calcium distribution in the body.
- It comes in two main forms: K1 and K2. Vitamin K1, also known as phylloquinone, is essential for blood clotting. Vitamin K2, or menaquinone, plays a crucial role in bone health and calcium metabolism.
- Beef liver is one of the best sources of this fat-soluble vitamin, with the heart, kidney, and pancreas also contributing notable amounts.

Water-Soluble Vitamins In Beef Organs
Water-soluble vitamins aren't stored in the body. To maintain their adequate levels, they must be consumed regularly. These vitamins play crucial roles in energy production and cellular growth and development.
Water-soluble vitamins found in bovine organs include B complex vitamins and vitamin C.
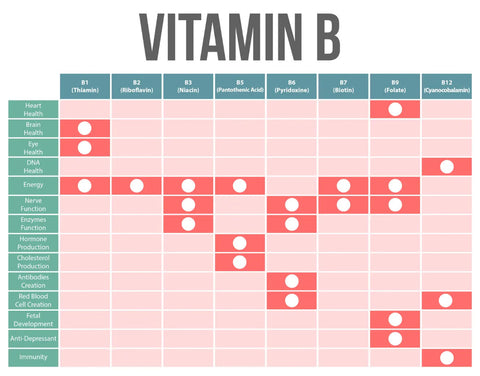
- Vitamin B1 (thiamin)
- Thiamin is crucial for energy metabolism and proper nervous system function, keeping you feeling energized and sharp.
- Beef liver is a thiamin treasure trove. Beef liver contains approximately 0.19 mg of vitamin B1 per 100g serving. This means a 100g serving of beef liver provides around 15.8% of the recommended daily intake (RDI) of thiamin.
- Other beef organs such as the heart, kidneys, and pancreas contain lower but decent amounts of B1.
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin)
- Riboflavin plays a key role in energy production, cellular growth, and metabolism, making it a must-have for overall health.
- The liver and kidney are excellent sources of riboflavin.
- Beef liver contains 2.76 mg, while the kidneys pack 2.84 mg per 100-gram serving. This means they provide around 213% and 218% of RDI respectively.
- Vitamin B3 (niacin)
- Niacin is essential for healthy skin, digestion, and nervous system function, making it a vital component of any well-rounded diet.
- Beef liver is a niacin powerhouse, but the heart, kidney, and pancreas are no slouches either.
- You can find around 13.2 mg of B3 in 100 grams of raw beef liver. The kidneys and the spleen contain around 8 mg each.
- The recommended daily intake of niacin is 16 mg/day for men and 14 mg/day for women. (Pregnant and breastfeeding women need around 18 mg of B3 every day.)
- Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid)
- This vitamin is crucial for energy metabolism, hormone synthesis, and the production of neurotransmitters that keep your brain and body in sync.
- You'll find pantothenic acid in all the major beef organs, with the liver being a particularly rich source.
- Beef liver contains 7.17 mg of pantothenic acid. The daily RDI for vitamin B5 is 5 mg.
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)
- Pyridoxine is essential for protein metabolism, red blood cell formation, and neurotransmitter synthesis, supporting overall physical and mental well-being.
- The liver, heart, and kidney are all fantastic sources of vitamin B6. A 100g serving of beef liver contains 83% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin B6.
|
Beef liver |
Beef heart |
Beef kidneys |
Beef pancreas |
|
1.08 mg per 100g |
0.279 mg per 100g |
0.665 mg per 100g |
0.2mg per 100g |
- Vitamin B7 (biotin)
- Biotin is crucial for healthy hair, skin, and nails, as well as proper metabolic function.
- Beef organs are excellent sources of this essential vitamin.
- The biotin content in 3 ounces of beef liver is equivalent to 103% of the recommended daily intake for biotin.
- Other bovine organ meats such as the kidney also contain high amounts of biotin, though slightly less than the liver.
- Vitamin B9 (folate)
- Folate is vital for DNA synthesis, red blood cell production, and fetal development. It’s a critical nutrient for overall health and pregnancy.
- Beef liver is exceptionally high in folate, containing around 290 mcg per 100g serving. This means a standard 3-ounce (85g) serving of beef liver provides approximately 215 mcg of folate.
- The folate content in a 3-ounce serving of beef liver represents over 50% of the RDI for folate, which is 400 mcg per day.
- Vitamin B12 (cobalamin)
- Vitamin B12 is essential for red blood cell formation, neurological function, and DNA synthesis, making it a crucial component of a healthy diet.
- Beef liver is a fine source of B12, but the kidney, heart, and pancreas are all excellent sources as well.
- 100 grams of liver meat provides 59.3 mcg of vitamin B12, which is about 988% of the DV.
- Beef kidneys contain 31.1 mcg of vitamin B12, while cow heart delivers around 8 mcg per 100 grams.
- Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
- Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect your cells from oxidative stress and supports a healthy immune system. It's also essential for the production of collagen, a protein that keeps your skin, bones, and connective tissues strong and healthy.
- Unlike other water-soluble vitamins, beef organs are not a significant source of vitamin C. The liver (often touted as a nutrient-dense organ) provides only trace amounts of vitamin C.
- Beef liver contains 1.3 mg per 100 grams. Beef heart contains around 6 mg, while kidneys provide approximately 7 mg of vitamin C per that amount.
- Grass-fed, pasture-raised beef organs may contain higher vitamin C levels.
We have an easy way for you to obtain your recommended daily intake of essential vitamins: order our beef organ capsules. With our convenient, easy-to-swallow capsules, you get the highest quality and purity without the dirty work.
Or, if you want to cook your own organ meats, learn how to prepare beef organs to rock your tastebuds.
Minerals In Beef Organs
Minerals are inorganic substances that have important roles in nearly all bodily functions. Beef organs are an excellent source of several essential minerals.
- Iron
- Iron is essential for the production of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout your body. Adequate iron intake helps prevent anemia, supports energy metabolism, and boosts immune function.
- Offal is a natural source of iron.
- Beef spleen contains the highest concentration of iron, with a 1.5g serving of freeze-dried spleen providing almost 100% of the RDI.
- The iron content in a 3-ounce serving of beef liver represents over 20% of the recommended daily intake for iron, which is 18 mg per day for adults.
- Beef kidneys contain around 3 mg of iron per 100g serving, while the heart has a moderate iron content of around 2.7 mg per 100g.

- Copper
- Copper works together with iron to form red blood cells and supports healthy bones, nerves, and immune function. It's also vital for the production of collagen and elastin, two proteins that keep your skin looking youthful and radiant.
- Beef liver is a copper powerhouse. It contains approximately 9.8 mg of copper per 100g serving. This represents a remarkable 488% of the recommended daily intake for copper.
- Selenium
- Selenium is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect your cells from oxidative stress and supports a healthy immune system. It aids thyroid function, as it helps convert thyroid hormones into their active form.
- Beef kidney, liver, and heart are all excellent sources of selenium, with the pancreas and spleen providing smaller amounts.
- Beef liver is an exceptionally rich source of selenium, containing around 31.5 micrograms (mcg) of selenium per 100g serving.
- Beef kidney also contains a high amount of selenium, with around 23-33 mcg per 100g serving.
Our beef kidney supplement will give your body a mega-dose of selenium, a powerful antioxidant that helps keep your immune system in tip-top shape and your thyroid humming along smoothly.
- Zinc
- Zinc plays a vital role in immune function, wound healing, and protein synthesis. It's important for growth and development, making it a crucial mineral for children and pregnant women.
- Beef liver, kidney, and heart are all excellent sources of zinc.
- Beef liver is exceptionally high in zinc, containing around 4.52 mg of zinc per 100g serving.
- Phosphorus
- Phosphorus is essential for building strong bones and teeth, as well as supporting proper muscle and nerve function. It increases the energy metabolic rate and the production of DNA and RNA.
- Beef liver, kidney, heart, and pancreas organs are all good sources of phosphorus, with the spleen providing a smaller amount.
- Beef liver is an excellent source of phosphorus, providing about 31% of the RDI per 3.5-ounce (100g) serving. This means a standard 3-ounce (85g) serving of beef liver contains around 155 mg of phosphorus.
- Beef kidney is also a rich source of phosphorus, containing around 228 mg per 2.5-ounce (75g) serving.

Other Nutrients Found In Beef Organs
Beef organs are not only rich in essential vitamins and minerals but also contain plenty of other beneficial nutrients. It’s no wonder they are dubbed the “nature’s multivitamin.”
Here's a list of some of the other noteworthy nutrients found in beef organs:
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)
- CoQ10 is a fat-soluble compound naturally produced by the body and found in every cell. It plays a crucial role in the production of cellular energy and acts as a powerful antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative damage.
- It supports heart health, protects against cardiovascular disease, boosts brain function, and supports healthy skin.
- Beef heart is one of the richest dietary sources of coenzyme Q10. It contains around 11.3 mg of CoQ10 per 100g serving.
- The CoQ10 content in the beef heart is about 2.9 times higher than in the liver and over 3.5 times higher than in regular beef muscle.

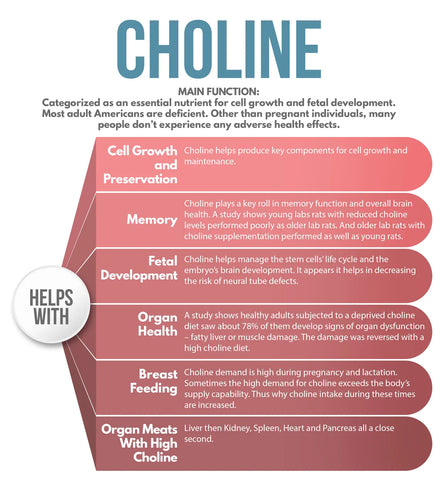
- Choline
- Choline is a water-soluble compound that is often grouped with B vitamins, although it is not technically a vitamin itself. It plays a crucial role in brain development, liver health, and nervous system function.
- Beef liver is an excellent source of choline, containing around 414 mg of choline per 100g serving. That represents over 64% of the recommended daily intake for this essential nutrient.
- Choline is also found in smaller amounts in the kidney, heart, and pancreas.
- Taurine
- Taurine is a sulfur-containing amino acid that is found throughout the body, with high concentrations in the brain, eyes, heart, and muscles. It supports cardiovascular health by regulating blood pressure, reducing inflammation, and protecting against heart disease.
- Taurine promotes brain function and acts as an antioxidant.
- Beef heart, liver, and kidney are all good sources of taurine.
- Beef heart contains around 46.3 mg of taurine per 100g of raw meat. Beef liver has about 46.3 mg, while the kidneys provide around 39.8 mg of taurine.
- Creatine
- Creatine is a naturally occurring compound produced in the body, primarily in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas, and stored in the muscles. It supports muscle growth and strength, while also improving memory and cognitive performance.
- Beef cuts, including organ meats, contain an average of 3-5 grams of creatine per kilogram of raw meat. Beef heart is an excellent source of creatine, containing around 46.3 mg of creatine per 100g.
When you incorporate beef organs into your diet, you can easily meet your daily requirements for key nutrients and give your body the tools it needs to thrive. Our convenient beef organ capsules deliver incredible health benefits of bovine liver, heart, kidney, and more.
Organ Meats vs Muscle Meat
While beef muscle meat such as steak and ground beef provides some essential vitamins and minerals, beef organs boast significantly higher levels of vitamins and minerals than muscle meat cuts. According to the Clinical Applications of Scientific Innovations (CASI), organ meats are more nutrient-dense than muscle meats on a pound-for-pound basis.
Here’s what that looks like in a chart that compares the nutrient profile of 100 grams of common beef organs and the same amount of beef and poultry meat (according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture).
|
Energy |
Protein |
Fat |
Ca |
Fe |
Mg |
P |
K |
|
|
Ground beef 90% lean |
185 kcal |
18.2g |
12.8g |
7mg |
2.13mg |
16.5mg |
148mg |
281mg |
|
Chuck roast |
232 kcal |
18.4g |
17.8g |
5mg |
2.06mg |
17mg |
151mg |
281mg |
|
Ribeye steak |
254 kcal |
18.7g |
20g |
4mg |
1.64mg |
16.7mg |
150mg |
288mg |
|
Tenderloin |
158 kcal |
22.2g |
7.07 |
28mg |
1.63mg |
23mg |
264mg |
340mg |
|
Beef liver |
112 kcal |
20g |
3.62g |
5mg |
4.9mg |
18mg |
387mg |
313mg |
|
Beef heart |
112 kcal |
17.7g |
3.94g |
7mg |
4.31mg |
21mg |
212mg |
287mg |
|
Beef kidney |
99 kcal |
17.4g |
3.09g |
13mg |
4.6mg |
17mg |
257mg |
262mg |
|
Chicken liver |
119 kcal |
16.9 |
4.83g |
8mg |
8.99mg |
19mg |
297mg |
230mg |
Let’s see why offal beats your average steak:
- The nutrients in organ meats may be more bioavailable and easier for the human body to use compared to muscle meats. That allows compounds from organ meats to enhance the absorption of minerals.
- Beef liver, heart, and kidneys contain higher amounts of B vitamins, iron, copper, selenium, and zinc than muscle meat.
- According to the Cleveland Clinic, organ meats are richer in fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K. Schmid and Walther reveal that offal “provides considerable amounts of vitamin D” and that the content in muscle meat is generally much lower.
- Beef organs provide beneficial compounds such as coenzyme Q10, conjugated linoleic acid, and glutathione that are not as abundant in muscle meats.
- Organ meats contain higher amounts of certain essential amino acids compared to muscle meats. They provide amino acids that have important regulatory functions in the body.
So, next time you're planning your meals, add some organ meats for a nutritional boost that can't be beaten. Your body will thank you.
What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Organ Meats?
Organ meats might not be the most popular cuts at the butcher shop, but they really should be. You’ve read the facts: offal is way more nutritious than traditional muscle meats such as steak or chicken breast. Cultures around the world have long valued organ meats for their nourishing properties and have incorporated them into their culinary traditions for generations.
Many people today are hesitant to embrace organ meats due to concerns and misconceptions surrounding their safety, taste, and preparation.
Here are some common misconceptions about organ meats:
Misconception: Organ Meat Is Unhealthy
Truth: Organ Meats Are Highly Nutritious
Beef liver, heart, kidneys, and other popular organ meats are rich in vitamins, minerals, essential fatty acids and amino acids, and a whole bunch of other essential nutrients. You can’t find some of them in muscle meat.
Misconception: Organ meat is high in cholesterol
Truth: Cholesterol in Organ Meats Has A Minor Impact On Blood Cholesterol
Organ meats do contain cholesterol, but dietary cholesterol from beef liver, heart, and other organs has less impact on the overall blood cholesterol levels. Saturated and trans fats play a much more significant role in raising harmful LDL cholesterol.
Your body naturally produces most of its cholesterol, and the amount it makes depends on how much you get from your diet (dietary cholesterol). When you consume more cholesterol from food, your liver produces less to keep things in balance. That’s why moderate amounts of bovine organs in a balanced, healthy diet won't significantly impact your blood cholesterol levels.
Misconception: Organ Meat Tastes Bad
Truth: The Taste Of Organ Meats Is Subjective (And Not So Bad Really)
What one person finds unappetizing, another may find delicious. It all comes down to personal preferences. Many traditional dishes around the world feature organ meats as a key ingredient not only for their exceptional nutritive values but also for their flavors.
For example, beef liver has a rich, slightly metallic flavor that some people love, while others may find it too strong. Beef heart has a taste that's similar to steak, but with a slightly more robust, gamey flavor. Kidneys have a more pronounced, slightly mineral-rich taste and a tender texture, but when prepared well, they can be quite delectable.
When properly seasoned and cooked, organ meats can be delicious.
Misconception: Only Certain Cultures Eat Organ Meat
Truth: Anyone Can Enjoy Organ Meat
Many cultures consume organ meats more frequently than others, but that doesn’t mean they can’t be part of a healthy diet for anyone, regardless of cultural background. Whether you grew up eating them or you're just curious to try something new, don't be afraid to give organ meats a chance.
Misconception: Organ Meat Is Difficult To Prepare
Truth: Easy-To-Follow Recipes Make Organ Meat Preparation Simple
Organ meats can be prepared using the same methods you'd use for your favorite cuts of steak or chicken, such as grilling, sautéing, or braising. You can incorporate them into pâtés, terrines, or stews or grind them for burgers.
Our keto cookbook is packed with easy-to-follow recipes that make preparing organ meats a breeze. Don't let the idea of cooking organ meats intimidate you—it's easier than you might think.
Misconception: Organ Meat Is Filled With Toxins
Truth: Healthy Animals Produce Safe-To-Consume Organ Meats
There is a concern that organs store toxins, making them unsafe to eat. The liver is a detox organ that filters toxins rather than stores them. As long as the animal is healthy and the meat is prepared properly, organ meats are safe to consume. The body of a healthy animal efficiently eliminates toxins, preventing their accumulation in the animal organs.
If you want to make sure your meat is 100% safe to consume, grass-fed beef is a top choice.
Animals raised on their natural diet of grass are less likely to accumulate toxins, as they are not exposed to the pesticides, herbicides, and growth hormones often used in grain-fed operations. Grass-fed beef organs ensure you're getting the highest quality organ meats available, so you can reap their nutritional benefits without any concern.
Why Are Grass-Fed Organ Meats More Nutritious?
Grass-fed organ meats offer a nutritional punch that sets them apart from conventional options. Here's why they're a superior choice for your optimal health:
- Grass-fed organ meat is even richer in nutrients. Grazing on lush pastures allows cattle to absorb a diverse array of vitamins and minerals from the soil, which then enriches their organs. This means higher concentrations of essential nutrients than their grain-fed counterparts.
- Grass-fed animals typically have lower levels of unhealthy fats such as saturated fat and omega-6 fatty acids, making their organ meats a heart-healthy option. This is also crucial for people who have to maintain balanced cholesterol levels.
- Grass-fed farming is free from hormones and antibiotics. This makes sure that the organ meats remain free from these harmful additives.
- Grass-fed organ meats have a richer flavor profile and tender texture, thanks to the natural diet and healthier lifestyle of the animals.
To get the highest quality and most nutritious supplements, we source our organ meats from grass-fed cows in New Zealand.
Why New Zealand?
Unlike many other countries, New Zealand has strict regulations against the use of growth hormones and antibiotics in cattle farming. This means that the beef from New Zealand is free from unwanted additives that can compromise quality and safety.
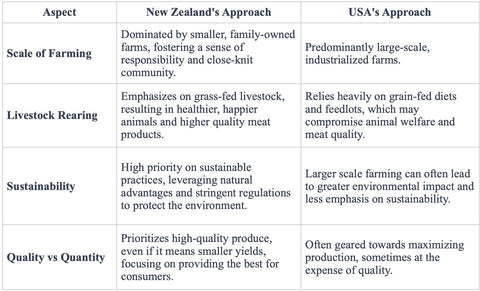
New Zealand's lush, green pastures provide the perfect environment for cattle to graze freely, resulting in healthier, more contented animals. This natural, grass-fed diet enhances the flavor and nutrient profile of the meat, making it richer in beneficial compounds such as omega-3 fatty acids, CLA, and vitamins A and E.
Read more about the benefits of New Zealand beef.
What Is the Healthiest Organ Meat?
Looking for the ultimate nutritional powerhouse in organ meats? Look no further than beef liver.
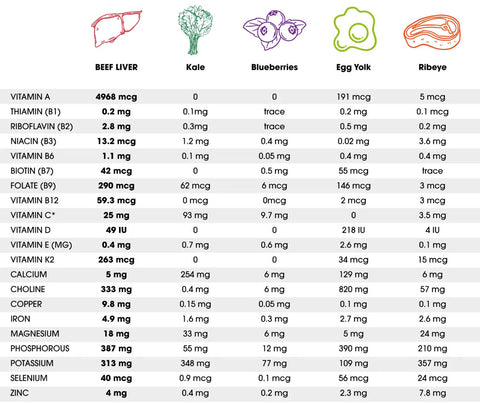
Here are some of the nutritious health benefits of liver:
- Beef liver is a vitamin A powerhouse for healthy vision, immune function, and reproductive health.
- Beef liver is packed with B vitamins for supercharged energy levels and brain function.
- Its highly bioavailable heme iron prevents anemia.
- The bovine liver is one of the top dietary sources of copper for collagen production, iron metabolism, and nervous system health.
- Grass-fed liver offers even more omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants.
- The liver is choline-rich for brain development, memory, and learning.
- Beef liver is a high-quality source of protein essential for muscle-building and weight management.
If you want to give your body and mind the ultimate nutritional support, our beef liver supplement is the obvious choice.
How Much Organ Meat Should I Eat?
The ideal amount of organ meat to consume depends on your individual needs and preferences. Some organ meat enthusiasts such as Dr. Paul Saladino suggest we should consume 3–5 ounces of organ meat every day. That might be too much for someone who’s just starting.
If you're new to organ meats, aim for 1–2 ounces per day, or a few larger servings per week. A smart strategy is to rotate different types of organ meat so you can benefit from their unique nutrient profiles. For example, the heart is a rich source of CoQ10, but the liver is loaded with vitamin A.
What if I Don’t Like Organ Meats?
Not everyone is a fan of organ meats. Whether it's the taste, smell, or texture, some people simply can't stomach them.
At One Earth Health, we've created a collection of high-quality, grass-fed organ meat supplements that offer all the nutritional goodness of organ meats in convenient, easy-to-swallow capsules. Our supplements are made from ethically sourced New Zealand cattle that are pasture-raised, grass-fed finished, and free from GMOs and hormones. They include several highly nutritious organ meats: beef liver, heart, kidney, pancreas, and spleen.
Where to Get the Best Grass-Fed Organ Supplements
We pride ourselves on offering top-tier grass-fed beef organ supplements sourced from ethical, small family farms. Our products contain no additives, fillers, or artificial ingredients—just pure nutritional goodness in convenient capsules.
Comparable to leading brands such as Ancestral Supplements and Heart & Soil, our supplements boast superior quality at a more accessible price point. Packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and high-quality protein, they address nutrient deficiencies often found in typical diets. Our supplements feature a potent blend of organs, providing concentrated nutritional support for your well-being.
Try our beef bone marrow supplement and experience a boost of nutrient-packed goodness that supports your joints, immunity, and vitality with each capsule. Our beef thymus supplement is a powerhouse for your immune system, helping you stay strong and healthy with every dose.
Experience the benefits of nose-to-tail nutrition without the hassle of preparing the meat yourself. Choose One Earth Health for the best grass-fed organ meat supplements and give your body the nutritional support it deserves.
Organ Meat FAQ
What are the best organ meats to start with?
Grass-fed, pasture-raised beef organs such as the liver, heart, and tongue are great options to start your culinary adventure. These organs have a mild flavor and can be easily incorporated into familiar dishes.
Beef liver has a unique, slightly metallic flavor that is more pronounced than regular muscle meat. Its texture is smooth and tender, with a melt-in-your-mouth quality when cooked properly. The key is to avoid overcooking it, as this can make it tough and intensify its strong flavor. Many people soak liver in milk or buttermilk before cooking to help mellow out the taste and create a more delicate flavor profile.
The heart has a distinctive flavor and texture that is more similar to lean muscle meat. It has a mild, slightly sweet taste with a chewy texture. When sliced thinly and cooked quickly over high heat, heart meat can be incredibly tender and juicy. Its taste is often compared to that of a lean steak, making it a more approachable option for those who may be hesitant about trying organ meats.
The beef tongue has a tender, creamy texture. Its flavor is often described as mild and beefy, with a slightly sweet undertone that is less intimidating than other organ meats. The tongue's high-fat content contributes to its rich, succulent texture, making it a deliciously indulgent option for those new to offal.
How much organ meat should I eat a week?
To reap the health benefits of organ meats, aim to consume about 4-6 ounces per week or roughly 10-20% of your total meat intake. This serving size allows you to benefit from the wide variety of vitamins, minerals, and other unique nutrients found in organ meats without overwhelming your taste buds or digestive system. Variety meats are nutrient-dense, so even small amounts can provide a powerful nutritional boost. When sourcing organ meats, choose high-quality grass-fed and organic organs for the best nutritional profile and distinctive flavor.
Does organ meat build muscle?
Organ meats can definitely help build muscle mass. They are an excellent source of high-quality, bioavailable protein and contain specific nutrients that support muscle growth, recovery, and metabolic health.
For example, the liver is a great source of preformed vitamin A, which plays a crucial role in protein synthesis and muscle building. The heart is rich in creatine, a compound that can enhance muscle strength, size, and power output. Organ meats also provide a wide range of B vitamins, zinc, and other nutrients essential for optimal muscle function and growth.
Why did we stop eating organ meat?
The popularity of organ meats has declined over the past century due to a combination of factors such as:
- Changes in cultural attitudes that favored muscle meats over offal
- Rise of modern agriculture
- Rise of processed foods
- Limited availability in grocery stores
- Lack of familiarity with organ meats
The modern Western diet has shifted focus to lean muscle meats, often overlooking the valuable nutrients found in organ meats. Some people may find the idea of eating organs unappealing or intimidating, as they are not commonly featured in mainstream cuisine. Limited availability in grocery stores and a lack of knowledge on how to prepare variety meats have also contributed to their decreased consumption.
Are organ meats superfoods?
Organ meats are often considered "superfoods" due to their incredible nutrient density and diverse health benefits. They are among the most concentrated sources of vitamins, minerals, enzymes, and other beneficial compounds, providing a wide range of essential nutrients in a highly bioavailable form.
Liver, for example, is one of the most nutrient-dense foods on the planet, offering ample amounts of vitamin A, B12, iron, copper, and choline. Beef heart is an excellent animal source of coenzyme Q10, a vital nutrient for cardiovascular health and energy production. The kidney is rich in selenium, a mineral with potent antioxidant properties.
What animal organs are not edible?
While most animal organs are edible and offer unique nutritional benefits, there are a few that are typically avoided due to potential health risks or undesirable taste.
- The brain and spinal cord of animals are generally not consumed, as they may carry a risk of transmitting certain diseases, such as prion diseases like bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) or "mad cow disease."
- The gallbladder is another organ that is not commonly eaten, as it can have a bitter taste and may contain concentrated toxins.
What organ meat is best for protein?
All organ meats are excellent animal sources of high-quality, easily digestible protein, but if you're looking for the best option, grass-fed beef heart is a top choice. Heart meat is lean, tender, and packed with bioavailable high-quality protein, making it an ideal option for those looking to build and maintain muscle mass.
A single serving of beef heart provides a significant amount of protein, along with a wide range of essential amino acids necessary for tissue repair, growth, and overall health. The heart also contains unique nutrients like CoQ10, which supports heart health, energy production, and physical performance.
How often should I eat organ meat on a carnivore diet?
A general recommendation is to include organ meats in at least 10-20% of your meals. Some carnivore dieters aim to eat variety meats every day, while others may consume them a few times per week. The frequency of organ meat consumption may vary depending on individual needs, preferences, and goals.
Rotate between different types of organ meats, such as liver, heart, kidney, and tongue, to get a balanced intake of nutrients. When sourcing organ meats, prioritize high-quality grass-fed and organic organs to maximize nutritional benefits. Listen to your body and adjust your organ meat intake based on personal tolerance and desired health outcomes.
Resources
Schmid, A., & Walther, B. (2013). Natural Vitamin D Content in Animal Products. Advances in Nutrition, 4(4), 453-462. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.113.003780
(2022, March 17). Exploring the Nutrient Density of Organ Meats. Designs for Health. https://www.casi.org/node/1536
FoodData Central. (n.d.). https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/index.html
Clinic, C. (2024, March 19). The Pros and Cons of Eating Organ Meat. Cleveland Clinic. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/organ-meat-benefits
Schmid, A., & Walther, B. (2013). Natural Vitamin D Content in Animal Products. Advances in Nutrition, 4(4), 453-462. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.113.003780





