Protein in Beef Organs
Posted by FAISAL TOOR
Want to supercharge your protein intake? Try adding beef organs to your diet.
Organ meats are some of the healthiest and most nutrient-dense foods on the planet, delivering a concentrated dose of high-quality, complete protein.

Article jumplinks:
Are beef organs high in protein?
Protein content in organ meats
What are the benefits of beef organ protein?
Can you overconsume organ meat?
What if I don’t like eating organ meat?
The benefits of beef organ supplements
What are the best beef organ supplements?
One Earth Health's beef organ supplement makes it easy to add these nutritional superstars to your diet. They contain grass-fed, pasture-raised liver, kidneys, heart, pancreas, and spleen, offering a convenient way to support muscle growth, boost energy levels, and improve overall health.
What Is Protein?
Protein is a very misunderstood concept. We’ll do our best to clear it up. To start with, we need to clarify the difference between “protein” as a general term, and “proteins” as a biological reality.
“Protein” vs “Proteins”
"Protein" is a macronutrient term that refers to the total concentration of individual proteins in a food. Individual proteins, in turn, collectively comprise a food’s protein content.
There are thousands of different proteins. For example, beef liver contains potentially hundreds of distinct proteins, including the following:
|
Albumin |
Aminotransferases (e.g., alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase) |
Carboxylesterases |
|
Catalase |
Collagen |
Cytochrome b5 |
|
Cytochrome P450 |
Elastin |
Ferritin |
|
Flavin-containing monooxygenases |
Globulin |
Glutathione peroxidase |
|
Glutathione S-transferases |
Heat shock proteins (e.g., HSP70, HSP90) |
Hemopexin |
|
Histones |
Metallothionein |
Myoglobin |
|
NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase |
Protein disulfide isomerase |
Retinol-binding protein |
|
Selenium-binding protein |
Serum amyloid A |
Superoxide dismutase |
|
Thioredoxin |
Transferrin |
When people ask “how much protein is in beef organs?” what they are actually asking is “what is the total concentration of all the different proteins in beef organs, collectively weighed against other macronutrients such as carbohydrates and fats?”
The answer: a lot. Beef organs are loaded with proteins, meaning they have a lot of protein.
Proteins Are Built From Amino Acids
Proteins are polymers: large, complex molecules composed of long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds, forming a linear sequence or chain. The specific sequence of amino acids in a protein is determined by the genetic information encoded in an organism's DNA.
There are 20 different amino acids that can be combined in different sequences to create an enormous diversity of proteins, each with its unique structure and function.
The 20 different amino acids that are commonly found in proteins are:
|
Alanine (Ala, A) |
Leucine (Leu, L) |
|
Arginine (Arg, R) |
Lysine (Lys, K) |
|
Asparagine (Asn, N) |
Methionine (Met, M) |
|
Aspartic acid (Asp, D) |
Phenylalanine (Phe, F) |
|
Cysteine (Cys, C) |
Proline (Pro, P) |
|
Glutamic acid (Glu, E) |
Serine (Ser, S) |
|
Glutamine (Gln, Q) |
Threonine (Thr, T) |
|
Glycine (Gly, G) |
Tryptophan (Trp, W) |
|
Histidine (His, H) |
Tyrosine (Tyr, Y) |
|
Isoleucine (Ile, I) |
Valine (Val, V) |
Some non-standard or non-canonical amino acids can be found in certain proteins, particularly in organisms other than humans, such as bacteria or plants. The 20 listed above are the most common and essential amino acids for protein synthesis in most living organisms.
These amino acids can be endlessly combined and recombined to create the vast diversity of proteins that exist.
Protein Structure
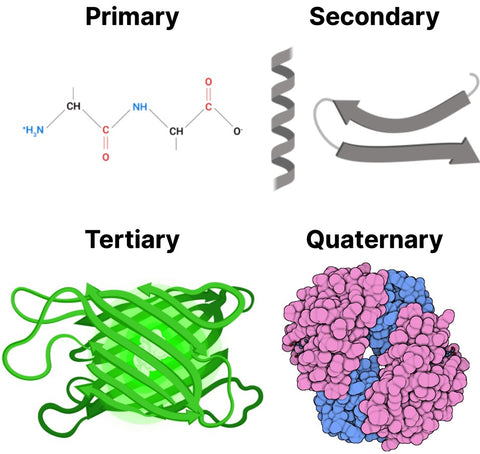
The structure of a protein is crucial for its function and can be described at four different levels:
- The primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain, held together by peptide bonds.
- The secondary structure refers to the local, regular patterns of folding or coiling within the polypeptide chain, stabilized by hydrogen bonds. The two most common secondary structures are alpha helices and beta sheets.
- The tertiary structure is the overall three-dimensional shape of the polypeptide. It results from the folding and coiling of the secondary structures, as well as interactions between different parts of the chain, such as disulfide bridges, ionic bonds, and hydrophobic interactions.
- The quaternary structure consists of multiple polypeptide chains, called subunits, that are arranged in a specific spatial configuration. The quaternary structure refers to the arrangement and interaction of these subunits.
Protein structure. Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Protein_Structure.png
A protein's function is determined by its unique three-dimensional shape formed by the folding of its amino acid chain. The specific sequence of amino acids in the chain and the chemical interactions between different parts of the chain drive this folding process. External factors such as pH, temperature, and the presence of other molecules in the environment also influence how the protein folds into its final three-dimensional structure.
What Do Proteins Do?
Proteins are essential for life, and their proper function is critical for maintaining good health. They have many functions within living organisms, including:
- Structural proteins provide mechanical support and structural integrity to cells and tissues, such as collagen in connective tissues and keratin in hair and nails.
- Enzymes act as biological catalysts, accelerating chemical reactions in the body without being consumed or altered.
- Transport proteins facilitate the movement of molecules across cell membranes or through the bloodstream.
- Regulatory proteins control and regulate cellular processes, such as gene expression, cell signaling, and metabolic pathways.
- Antibodies are produced by the immune system that recognize and neutralize foreign substances (antigens). They protect the body from pathogens and diseases.
- Motor proteins are involved in the movement of cellular components, such as actin and myosin, which are responsible for muscle contraction and cellular motility.
Protein gives your body the essential amino acids to build its own proteins. Make sure to include protein-rich foods in your diet to keep your body functioning properly.
How Much Protein Does the Average Person Need?
According to the Mayo Clinic, the average sedentary adult needs 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. This means:
- The average sedentary man needs around 56 grams of protein per day
- The average sedentary woman needs around 46 grams of protein every day
This depends on the activity level, age, muscle mass, and overall health status of the individual.
- If you exercise regularly, you may have higher protein needs, around 1.1-1.5 grams per kilogram of body weight.
- If you lift weights or train for endurance events, you may need 1.2–1.7 grams per kilo.
- As people age (40-50+), protein needs increase to around 1–1.2 grams per kilogram to prevent loss of muscle mass.
Are Beef Organs Good Sources of Protein?
Beef organ meat is an excellent source of protein. They may not be as popular as muscle meats, but beef organs provide a more concentrated source of high-quality protein and other important nutrients such as minerals and vitamins.
The proteins found in beef organs are complete proteins containing all the essential amino acids our bodies cannot produce on their own. Many other sources of protein such as legumes, grains, vegetables, and some other plant-based foods are incomplete, meaning they lack one or more of the essential amino acids that must be obtained from the diet. With beef organs, you can be sure you're getting an abundant supply of crucial complete proteins.
Their rich flavor and nutrient density make organ meats exceptionally keto-friendly. They’re dense in protein and healthy fats, and low in carbs. Plus, their high biological value means the proteins from organ meats are easily used by the body to support muscle synthesis on a low-carb lifestyle.
When you eat beef organs, you use more of the animal and reduce food waste. This ethical approach to meat consumption maximizes the resources used in raising livestock. At One Earth Health, we’re passionate advocates of regenerative farming which rebuilds soil health, sequesters carbon, and promotes biodiversity.
We source our beef from grass-fed cattle raised on New Zealand pastures. When you choose our products, you get all the nutritional benefits of nose-to-tail eating in a convenient, easy-to-consume form. Order our beef organ supplement and discover nature's most nutrient-dense source of protein.
Protein Content in Beef Organs
Beef organs pack an impressive amount of high-quality protein into a relatively small portion. Here’s how much protein 100 grams of the most common organ meats contains, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA):
|
Beef liver |
20g |
|
Beef heart |
17.7g |
|
Beef pancreas |
15.7g |
|
Beef kidneys |
17.4g |
|
Beef spleen |
18.3g |
|
Beef thymus |
12.2g |
|
Beef trachea |
53.14g |
|
Beef bone marrow |
19.4g |
Protein in Beef Liver
Beef liver is an excellent source of protein, with around 20 grams of complete, high-quality protein per 3.5-ounce (100g) serving.
Beef liver contains more nutrients, gram per gram, than any other organ. It's particularly high in vitamin A, riboflavin, folate, iron, and copper. As the most nutrient-dense of all beef organs, the liver provides an incredibly concentrated source of proteins, vitamins, and minerals that are difficult to obtain from other food sources.
As the most protein-packed and nutritious offal, beef liver offers a plethora of health benefits.
Try our grass-fed beef liver supplement and unlock a treasure trove of nature's most potent nutrients. This superfood in a capsule will nourish your family with the ancient power of beef liver.
Protein In Beef Heart
As a lean and flavorful muscle meat, beef heart is an excellent source of complete proteins. The proteins in beef heart are highly bioavailable, meaning they are efficiently absorbed and used by the body. Beef hearts have a meaty texture and rich, nutrient-dense profile, making them a healthy and affordable way to boost your protein intake.
Protein In Beef Kidneys
The protein found in beef kidneys is a high-quality, complete source containing all the essential amino acids. Kidneys also provide an excellent dose of nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, riboflavin, and selenium.
When you add kidneys to your diet, you may also support healthy blood formation, immune function, and antioxidant activity. Here’s more about the benefits of beef kidneys.
We harnessed the nutrient-dense superpowers of beef kidneys and created the best grass-fed beef kidney supplement. For those sensitive to the taste of bovine kidneys, this is the most convenient, cooking-free way to support healthy energy levels, blood formation, and overall vitality.
Protein In Beef Pancreas
While not as popular, the beef pancreas is another rich source of protein. The pancreas is an excellent way to add variety to your diet while taking advantage of this often overlooked but nutritious organ meat.
The beef pancreas is a concentrated source of minerals essential for metabolic functions and a strong immune system. Read all about the health benefits of beef pancreas.
Protein In Beef Spleen
Beef spleen packs around 18 grams of protein into every 3.5-ounce serving. Often neglected in modern diets, this organ meat represents an underrated nutritional goldmine. The spleen's dense protein content is complemented by an array of B vitamins, iron, zinc, and other essential nutrients.
The savory flavor and velvety texture of beef spleen allow for easy incorporation into a wide range of dishes from cultures around the world.
Read more about the benefits of bovine spleen.
If you want to enjoy the benefits of all these amazing organ meats packed with protein and essential nutrients, our beef organ capsules are the way to go. These supplements deliver a highly bioavailable source of complete proteins, vitamins, and minerals from beef liver, heart, pancreas, kidney, and spleen.
Protein In Beef Thymus
Beef thymus packs a serious protein punch. But the thymus is more than just a protein powerhouse; it's also rich in vitamin B12, iron, and zinc that support a healthy immune system. When you incorporate this nutrient-dense delicacy into your diet, you'll be treating your body to an array of vital proteins, minerals, and antioxidants that promote overall vigor and vitality.
We have just the thing that can help you achieve vitality and boost your immune system. Our beef thymus supplements harness the concentrated nutritional power of the organ, delivering a potent blend of complete proteins, B vitamins, iron, and zinc to fortify your body's defenses.
Protein In Beef Trachea
You’ll be amazed by the amount of protein found in beef trachea: this overlooked organ delivers a staggering 53 grams of high-quality protein per 100-gram serving when air-dried. The trachea isn't just a protein bomb; it's also an excellent source of minerals such as phosphorus and magnesium that support bone health and energy production.
With its high protein density and rich nutrient profile, the trachea represents an economical way to supercharge your diet with the building blocks for strength and vitality.
Upgrade your protein game with our beef trachea supplement. Each serving packs an incredible 20 grams of complete, bioavailable proteins into an easy-to-consume capsule.
Protein In Bone Marrow
Beef bone marrow is a great source of protein. It packs more protein per 100 grams than beef pancreas, kidneys, and thymus. Sure, it's a bit high in calories due to the fat content, but that rich, flavorful marrow is totally worth it.
Bone marrow offers other benefits such as plentiful amounts of vitamins A and K2, as well as iron and zinc, making it a nutritious addition to your diet. Some people avoid the taste and the smell of bone marrow, so they turn to our grass-fed beef bone marrow supplements. They help you get your share of protein, collagen, and beneficial fatty acids that support joint health, skin elasticity, and gut health.
What Are the Benefits of Beef Organ Protein?
Beef organs have all 20 essential amino acids, including the 9 that the body cannot produce on its own. Here are the key benefits of the protein and amino acids found in beef organ meats:
- The high-quality protein in beef organs supports the growth and repair of lean muscle mass, which is essential for maintaining strength and mobility.
- Amino acids such as glycine and proline, abundant in organ meats, are crucial for the repair and regeneration of tissues throughout the body, including skin, bones, and cartilage.
- The amino acids in beef organ protein are necessary for the production of hormones and enzymes that regulate bodily functions, such as digestion and metabolism.
- Glutamine and arginine from organ meats play a vital role in supporting immune function and reducing inflammation.
- The high protein content in beef organs can help keep you feeling full and satisfied, aiding in weight management and reducing cravings.
Protein Content in Organ Meat vs Muscle Meat
While beef organs are packed with protein, muscle meats contain a slightly higher concentration of protein per gram. With that said, offal is still more nutrient-dense overall. Here’s why:
- Organ meats are rich in essential vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin A, B vitamins (especially B12), iron, copper, and zinc, which are crucial for nearly all bodily functions.
- The nutrients found in organ meats are often more bioavailable than those in muscle meats, meaning they are more easily absorbed and used by the body.
- Organ meats contain specific nutrients that are not as abundant in muscle meats, such as CoQ10 in the heart, vitamin K in the liver, and choline in the brain and liver.
- Organ meats are a source of other beneficial compounds: carnitine, creatine, and taurine support energy production, brain function, and cardiovascular health.
- Some organ meats such as the liver provide essential fatty acids like omega-3 fatty acids. They are important for brain health and reducing inflammation.
If you're sticking to a high-protein or keto diet, beef organs are a great choice—alongside muscle meats. While organs may have slightly less protein per gram, they more than make up for it with their nutrient density. For the best results, pair your beef with plenty of low-carb veggies, healthy fats, and other nutrient-rich foods to create a well-rounded, balanced diet that supports your health.
For some tasty inspiration, be sure to check out our free keto cookbook. It's packed with 80 delicious, easy-to-make meals that'll keep you on track and loving every bite.
Can You Eat Too Much Organ Meat?
It is possible to eat too much organ meat. All organ meats, especially the liver, are incredibly nutritious, so consuming them too often or in excess can lead to some potential health risks such as:
- Beef liver is an exceptional source of vitamin A, but too much of this vitamin can lead to vitamin A toxicity, causing symptoms like nausea, hair loss, and potentially liver damage.
- Organ meats are high in purines, which can contribute to the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. Increased uric acid causes or exacerbates gout.
- Organ meats are very high in iron. Too much organ meat can deposit iron in your system, leading to a condition called hemochromatosis. This is associated with joint pain and liver dysfunction.
- Beef organs are high in cholesterol. High cholesterol levels may be a concern for those who suffer from cardiovascular disease or are managing high blood pressure.
Try not to over-consume any single organ for extended periods without rotation or balance in the diet. Add bovine organs to your weekly menu as part of a broader, balanced diet for maximum benefits without overdoing any single food.
What if I Don’t Like Eating Organ Meat?
The distinctive taste and aroma of beef organ meats can be an acquired taste. Their flavors are often described as strong, earthy, and somewhat metallic. The texture of organs is quite different from your regular steak, with a softer, more tender consistency which might not be everyone's cup of tea.
Plenty of people enjoy the rich, robust taste of a well-prepared liver or kidney, but others aren't accustomed to the intense flavor and unique aroma. Our grass-fed, 100% organic beef organ supplements offer a convenient solution.
Our carefully formulated capsules, sourced from New Zealand free-range cattle, allow you to reap the benefits of organ meats without the flavors or textures.
Benefits of Beef Organ Supplements
If you're looking for a convenient way to get all the nutritional goodness of organ meats without the fuss, One Earth Health's beef organ supplements are exactly what you need. Here are some of the amazing health benefits you can expect from our supplements:
- Our supplements make it easy to get your daily dose of vitamins, minerals, and all other essential nutrients.
- The high levels of zinc and vitamin A in our supplements can help give your immune system a boost, keeping you healthy and resilient.
- Packed with B vitamins and CoQ10, our organ meat capsules can help support your body's energy production, leaving you feeling vibrant and energized.
- The collagen and other nutrients found in organ meats can help keep your skin, hair, and nails looking their best.
- Choline and other compounds in our supplements may support cognitive function and brain health.
- The CoQ10 and other nutrients in organ meats have been shown to support cardiovascular health.
- Bioactive compounds in bovine connective tissues and collagen aid vitality and healthy aging cellular processes over time.
- Looking to bulk up and build some serious muscle? Loaded with high-quality, bioavailable protein, our supplements can support your gains and take your fitness to the next level. Whether you're a hardcore athlete or just looking to maintain a healthy, active lifestyle, the nutrients in our organ meat capsules can help keep your muscles fueled, boost recovery, and stay ready to tackle any challenge.
If you want to experience the many benefits of organ meats without the strong taste or unique texture, give One Earth Health a try.
Get the Best Beef Organ Supplements
The standard American diet is pretty much a nutrient wasteland, with too many carbs and unhealthy fats, and not nearly enough protein and essential vitamins and minerals. Our organ meat supplements give you a concentrated dose of quality protein and nutrient density in every capsule.
We only use the best grass-fed and organic beef raised in New Zealand, where the cattle roam freely on lush, green pastures. These organs come straight from small family farms, so you know you're getting the real deal. We don't add any sketchy fillers, artificial junk, or unnecessary additives. Just pure, unadulterated nutritional goodness in a convenient capsule form.
Experience the benefits of nose-to-tail nutrition without the hassle of preparing the meat yourself. Choose One Earth Health for the best grass-fed beef organ supplements and give your body the nutritional support it deserves.
Beef Organ Protein FAQ
Are beef organs high in protein?
Beef organs are nutritional powerhouses high in protein. They offer a plethora of essential nutrients, including high-quality amino acids, fat-soluble vitamins, vitamin B2, vitamin B6, and omega-3 fatty acids, all in a bioavailable form. These nutrients work synergistically to support overall health, from the formation of healthy blood cells to the maintenance of strong bones and muscles.
Which organ has the highest protein?
Among beef organs, the trachea generally has the highest protein content. A 100-gram serving of beef trachea provides around 50 grams of protein. The second protein-rich organ is the liver, delivering 20 grams of protein per 100 grams of raw meat. The liver is also an excellent source of vitamin B2, vitamin B6, and fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamin A and vitamin D. Variety meats such as the heart and kidney also provide a significant amount of protein, along with other essential nutrients like vitamin B2, vitamin B6, and non-heme iron.
How much protein is in beef organs?
Different beef organs have different protein concentrations. Here are some average values per 100 grams:
- Beef liver: 20-22 grams (also rich in vitamin B2, vitamin B6, and fat-soluble vitamins)
- Beef heart: 17-18 grams (a good source of omega-3 fatty acids and CoQ10)
- Beef kidney: 15-17 grams (high in vitamin B2, vitamin B6, and minerals like iron and zinc)
- Beef tongue: 16-18 grams (a good source of zinc and vitamin B12)
- Beef tripe: 12-14 grams (rich in protein and low in fat, with a unique texture)
Does organ meat build muscle?
Variety meats can help you build muscle due to their high-quality protein content and the presence of essential nutrients that aid protein metabolism. The protein found in organ meats is highly bioavailable, allowing the body to easily absorb and utilize it for muscle growth, repair, and maintenance. The fat-soluble vitamins and omega-3 fatty acids found in organ meats support overall muscle health and function.
Are all organs made of protein?
While all organs contain a significant amount of protein, they are not solely made of protein. Organs are complex structures that consist of various types of tissues, each with its unique composition. In addition to protein, organs also contain fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. For example, the liver is a rich source of fat-soluble and water-soluble vitamins, while the heart contains omega-3 fatty acids.
Does excess protein turn into fat?
Excess protein beyond your body's needs does not directly turn into fat. When you eat more protein than your body requires, the excess amino acids are typically broken down and used for energy or excreted. If you consistently consume more calories than you burn, the excess energy can be stored as body fat, regardless of the macronutrient source.
Is beef the king of protein?
Beef, particularly offal such as liver, heart, and kidney, can be considered a "king of protein" due to their high protein content and nutrient density. Beef organs offer a concentrated source of high-quality protein, along with other essential nutrients like fat-soluble vitamins, vitamin B2, vitamin B6, and non-heme iron. These nutrients work together to support bodily functions, from the formation of healthy blood cells to the maintenance of strong muscles and bones.
What vitamins are found in beef organs?
Beef organs are rich in vitamins, including fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin A, vitamin D, and vitamin K2. They are also excellent sources of B vitamins, such as vitamin B1 (thiamine), vitamin B2 (riboflavin), vitamin B6, vitamin B12, pantothenic acid, and folic acid. These vitamins play crucial roles in maintaining optimal health and supporting functions like blood cell production, energy metabolism, and reproductive health.
Do many people eat beef tongue and tripe?
Beef tongue and tripe are popular meat cuts worldwide, particularly in cultures where nose-to-tail eating is common and organ meats are considered traditional delicacies. In some countries, such as Mexico, the tongue is a popular ingredient in dishes such as tacos, while tripe is often used in soups and stews.
In modern Western diets, the consumption of organ meats has declined, and they are often viewed as less desirable cuts of meat. Despite this, there is growing interest in the nutritional benefits of organ meats, and some dietary programs, such as the ketogenic diet, emphasize the importance of incorporating these nutrient-dense foods into the diet.
Which proteins from beef organs can support cardiovascular health?
Beef organs contain several proteins and nutrients that can support cardiovascular health. One notable example is CoQ10 (coenzyme Q10), which is found in high concentrations in the heart and liver. CoQ10 is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect the heart and blood vessels from oxidative stress, supporting optimal heart function.
Beef organs are a rich source of alpha-lipoic acid, another antioxidant that has been shown to promote heart health by reducing inflammation and improving endothelial function. The high-quality protein found in organ meats, along with other nutrients like iron and B vitamins, also contributes to overall cardiovascular health by supporting the maintenance of healthy blood cells and blood vessels.
Resources
Weiss, C. (2023, June 15). Mayo Clinic Q and A: Protein needs for performance. Mayo Clinic News Network. https://newsnetwork.mayoclinic.org/discussion/mayo-clinic-q-and-a-protein-needs-for-performance/
Torrella, K. (2024, January 30). How much protein should I eat per day? Why Americans are obsessed with eating protein-rich diets. Vox. https://www.vox.com/future-perfect/24049505/protein-intake-fiber-plant-based-vegetarian-vegan-meat
FoodData Central. (n.d.). https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/